DDoS attacks are a fact of life, and no company is immune to them. During an attack, the system is flooded with a huge number of requests. When mass requests exceed the acceptable level, the server becomes unavailable.
In this article, we describe everything you need to know about DDoS attacks: what they are, the different types, and the best ways to protect your online resources.
What is a DDoS
A DDoS attack is a deliberate attempt to overwhelm a network's resources with an infinite number of requests, which it cannot handle.
They are limited by the allowable server load and bandwidth. If there are too many requests, it will reduce performance or stop the network resource completely. This is what happens: it's called a denial of service attack, or DoS for short.
DDoS is a special case of DoS and is a distributed denial of service attack. In the case of a DoS attack, the attacker sends traffic to the victim through a single Internet connection. In contrast, DDoS is a much more extensive attack. It involves thousands, if not millions, of connected devices. DDoS is much more difficult to deal with.
A DDoS attack is a type of cybercrime in which an attacker sends a stream of Internet traffic to the server under attack, preventing ordinary users from accessing the resource.
There is no one single reason behind DDoS. Disgruntled individuals or groups seeking to express their displeasure towards a company or resource can carry them out. Alternatively, they can be employed to disable the work processes of a competitor's company. Attacks can also be used for the purpose of extortion or damage to a rival's reputation.
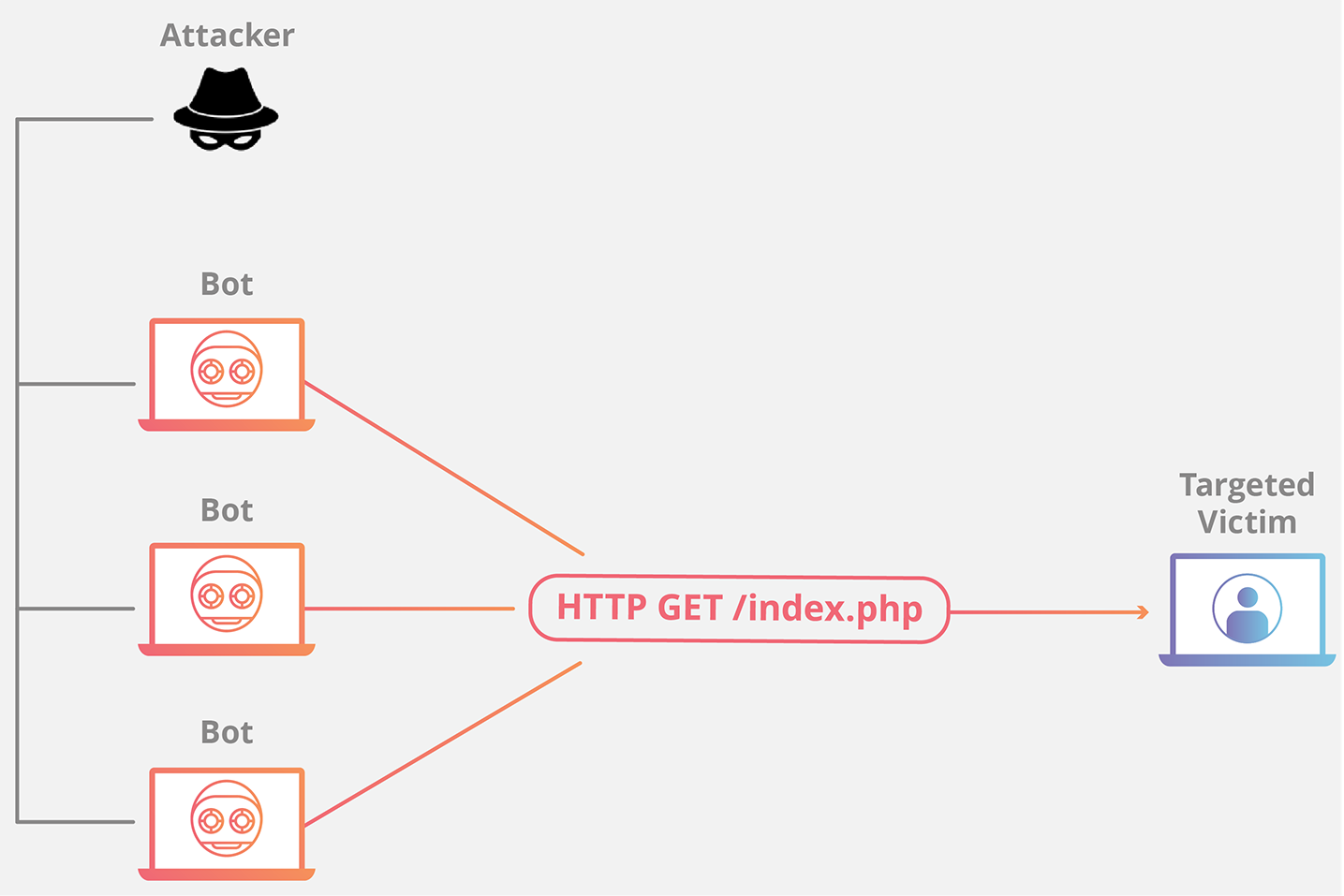
The most common method of carrying out an attack is through the use of botnets. An attacker hacks into computers and other devices and installs malware or code fragments called bots. A network of such infected devices is called a botnet.
Next, the attacker sends the botnet a command to overload the servers with connection requests. The number of requests far exceeds what the servers can handle.
How to recognise a DDoS attack
The problem with identifying attacks of this type is that there are no specific signs of them. Especially from the outside. Most internet users experience slow loading speeds of websites, excessive spam, and inaccessible pages almost daily. This could all be a symptom of a DDoS, but it also could be the result of completely different causes.
The duration of the problem is also difficult to identify, as it can last as little as an hour, or last for months. The intensity can also fluctuate.
If you suspect a DDoS attack, you should be aware of the following signs:
-
If you notice that a website or online service is inaccessible or running too slowly, you can be sure that a DDoS attack is underway. Monitor the site's performance with a tool or open it from different browsers and devices.
- Check for unusual traffic on the server. Review the server logs to determine if there is an unexpected increase in traffic. If you notice an unusually high number of requests from certain IP addresses or to any specific pages, you can be sure that this is a DDoS attack.
-
Denial of service for legitimate users. Ask users to report any access problems to you immediately so you can respond quickly.
-
Look out for unexpected spikes in resource usage, such as CPU time, memory, or network bandwidth. System resource monitoring will help you quickly detect any anomalies.
-
You must report any anomalous activity. Security monitoring services and DDoS defence services will notify you of any anomalous activity.
Types of DDoS attacks
Attacks are divided into three types:
-
By OSI model;
-
By protocol;
-
By mechanism.
Network connectivity consists of 7 different layers (OSI Model) and DDoS attacks can target different parts of the network. Therefore, they are usually classified based on the layer of connectivity the attack is targeting.
-
It is not possible to launch a DoS or DDoS attack at the physical layer.
-
At the link layer, MAC flooding attacks are possible. In this case, the data packets overload the network switches, causing all ports of the connection to fail.
-
At the network layer, attackers overload the network with ICMP flooding. This reduces the network bandwidth and the number of requests that can be received.
-
At the transport layer, DDoS attacks using Smurf and SYN flooding are the most common. These attacks exceed the thresholds in terms of channel width and number of available connections.
-
At the session layer, an attacker exploits software weaknesses via Telnet protocol, which allows them to gain access to the server.
-
At the presentation layer, attackers create garbled SSL requests to conduct attacks on the server. Validating encrypted SSL packets is a time-consuming task that slows down resources.
-
At the application layer, attacks are carried out using malware. A huge number of requests are created, so-called HTTP flooding, which causes the resource to overload and normal users cannot access it.
By protocol, there are three major groups of network protocols commonly distinguished:
-
UDP;
-
TCP;
-
Others (ICMP, GRE, ESP, AH, SCTP, OSPF, etc.).
There are a number of attacks that can be carried out on a network. These include IP Null, where a zero is written in the IP packet field instead of the protocol information, which allows the firewall to be bypassed. Another is SYN flooding, where spamming connection requests to the server overloads the server connection table memory. UDP flooding is another attack, where the server is flooded with a large number of UDP packets from different IP addresses. Finally, there is the ping of death, where the ping command generates packets that are either incorrectly generated or simply too large.
By mechanism
We can distinguish three types of attacks according to their mechanism:
-
Flood-based. These attacks involve flooding the communication channel. This includes DNS amplification, fragmented UDP flooding, ICMP flooding, etc.
-
Exploitation of vulnerabilities in the network protocol stack. These include attacks that modify the TOS field, spoofed TCP sessions with multiple SYN ACKs, RST, FIN flooding, etc.
-
Application layer. This category includes HTTP flooding, application denial of service attacks, fragmented HTTP packet attacks, etc.
Anti-DDoS solutions
Protecting against DDoS attacks is not easy. Even large, world-famous companies are affected by DDoS attacks from time to time. Therefore, it is important for organisations to take measures to protect against and respond to DDoS.
-
Develop a plan for responding to an attack. Write instructions for employees, describe the priority areas of defence.
-
Use a CDN (content delivery system). This allows you to reduce the load on servers and redistribute traffic.
-
Use the services of a professional DDoS protection provider.
-
Use not only a firewall, but also additional tools such as WAF (offers more fine-tuning and can detect more threats).
-
Use the CAPTCHA on the site to filter out bots and reduce server load.
-
Organize continuous traffic monitoring and analysis.
If an attack occurs, start implementing your plan and contact your DDoS protection provider.



