PCI DSS, or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, sets out security requirements for organizations that process payment card transactions. In this article, we will look at the key components and principles of the PCI DSS security architecture.
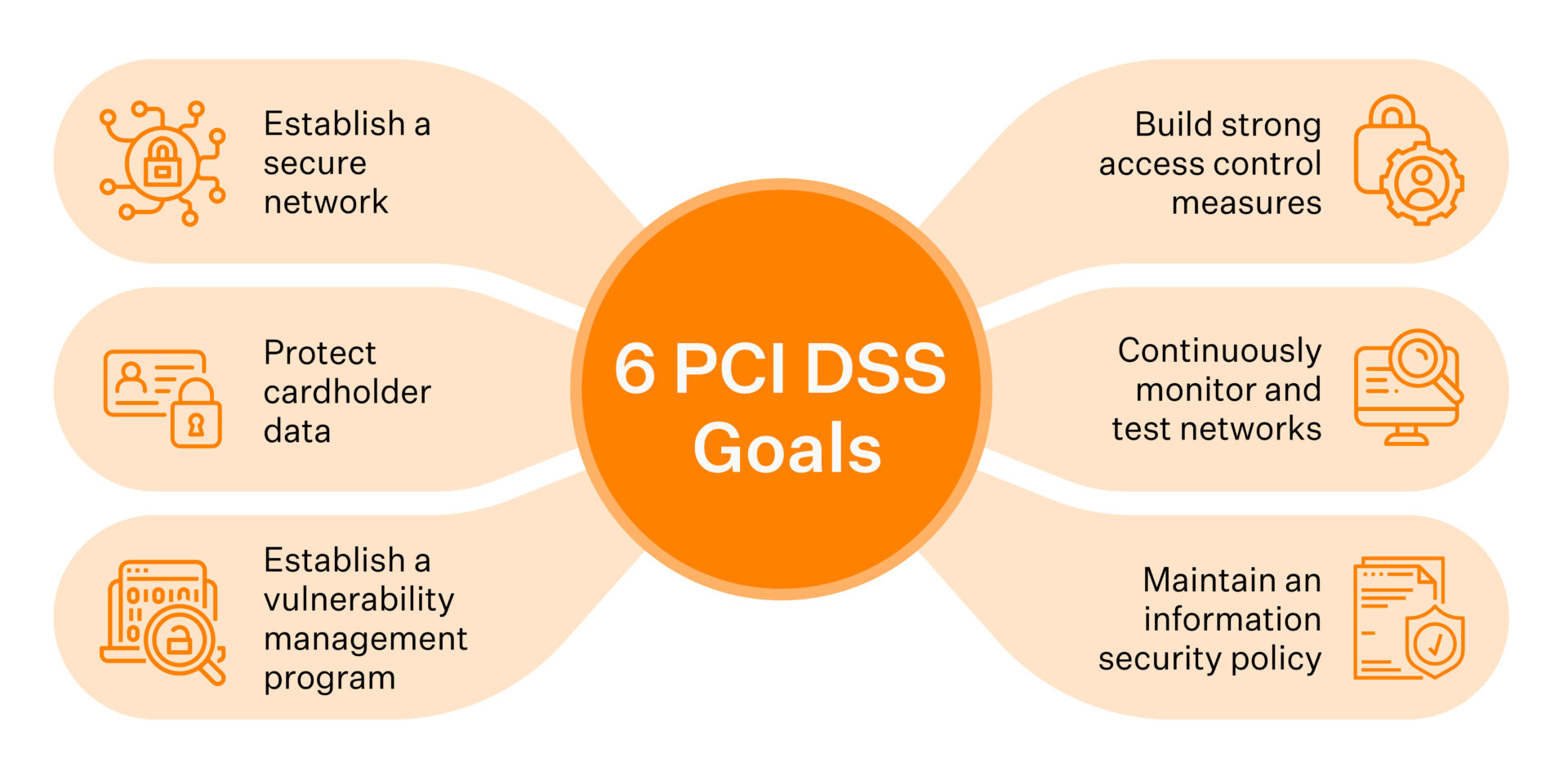
6 PCI DSS principles
Adhering to the core principles of the PCI DSS will help you create a robust security environment, keep your data safe and your business running smoothly.
-
Establish and maintain a secure network and systems.
-
Protect cardholder data.
-
Maintain a vulnerability management program.
-
Implement strong access control measures.
-
Regularly monitor and test your network.
-
Support an information security policy.
The requirements for a security architecture
1. Firewalls. These devices control traffic according to criteria set by configuration. They can protect the network from illegal intrusions and malware.
There are hardware firewalls and software firewalls. The former are physical, protecting and segmenting the network. To work properly, they need to be correctly configured and then regularly maintained. This is the only way hardware firewalls can work effectively. Software firewalls protect against insider threats, such as phishing attacks. They are much easier to maintain and less expensive.
To build a secure architecture, firewalls must be installed on all devices that access the network.
2. Change default passwords. Sometimes applications have default logins and passwords. They are very simple, either easy to guess or known. Change them immediately after installation. We also recommend using a password generator to create stronger password combinations.
3. Do not store customers' personal information unnecessarily. Sometimes personal account numbers (PAN) are left unencrypted on websites. Avoid this by promptly deleting data not required for regulatory, legal or business purposes. If you store account numbers, keep them encrypted.
To detect unencrypted data in a timely manner, you need to run data discovery tools regularly. Once discovered, you should either delete or encrypt the data.
4. Encrypt data transmissions over open public networks. Any transmission of cardholder data over open or public networks should be encrypted to prevent it from being compromised. A secure encryption method with appropriate security protocols should be used to protect against theft or intrusion. Personal account numbers should not be sent via messaging platforms, SMS or email.
5. Update anti-virus software regularly. Outdated anti-virus software is a poor barrier to system infection. To ensure effective protection, you should update as new databases are released. It is also important to set up regular scans and audit logs.
Users should not have sufficient access rights to disable anti-virus software themselves.
6. Support secure systems and applications. The organization should have a system for regular patch management. Operating systems, firewalls, Internet browsers and application software are subject to regular patch updates.
Timely implementation of security updates is key to ensuring data security. Installing critical patches within one month of their release is a PCI DSS compliance requirement.
7. Limit employee access to cardholder data. To ensure the security of sensitive data, employees should only be granted access based on business need. Users should have the minimum access and privileges necessary to do their jobs.
Prevent unnecessary disclosure of cardholder data by configuring administrator and user accounts in a role-based access control system. The system defines roles and levels of privileges. It maintains an active list of personnel with appropriate access to cardholder data.
8. Identification and authentication of access to system components. Traceability of access should be ensured. The assignment of unique usernames to authorised personnel allows traceability of system use in the event of data compromise. The sharing of identifiers should be strictly prohibited.
The use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) to identify users is mandatory as an additional layer of PCI DSS security. You can implement MFA in one of the following ways
-
What the user knows, like PINs or passwords
-
What the user has, such as an SMS code or USB token
-
Who the user is, such as fingerprints or facial recognition
9. Restrict physical access to cardholder data. Do not store cardholder data in an open, easily accessible environment. Physical access to data should be restricted to prevent internal theft of information (by employees, contractors and consultants). Use badges for visitors or temporary workers to reduce the risk of data disclosure.
On termination of employment, any physical items that provide access (such as keys or access cards) should be deactivated or returned. Train your staff regularly on security procedures.
10. Track, monitor and report on all access to network resources and cardholder data. Tracking systems are useless unless logs are reviewed for suspicious activity. Without accurate logs of system activity, it is almost impossible to determine the reasons why a system has been compromised.
Therefore, it is critical to train employees on how to properly track, monitor and interpret security alerts, and then take appropriate corrective action.
-
System logs and audit trails should be checked and retrieved daily:
-
User access to cardholder data
-
Actions taken by employees with administrative privileges
-
Invalid access attempts
-
ID and access changes.
11. Regular system and process security testing. In addition to routine system monitoring, regular system and process testing helps the organization stay ahead of security threats and vulnerabilities. Ensure that security measures are effective and compliant by proactively testing system controls.
In addition to regular testing, perform additional testing when system configurations change or new software is deployed. Vulnerability scans and penetration tests identify potential threats and are important for maintaining system integrity.
The frequency of these scans and tests will depend on the infrastructure and size of the organization.
12. Maintain an information security policy and risk assessment for all employees. They must understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining the required security standards. The organization should take the security of cardholder data seriously to ensure compliance with PCI DSS requirements.
Maintaining a strong security policy sets expectations for employee performance in relation to risk management. Review and update it annually to reflect changes in the system or environment. Regular risk assessments can help identify critical assets and vulnerable areas.



