A cluster is a group of hosts configured to share their resources. On the VMware vSphere virtualization platform, you can create two types of clusters: High-availability Cluster (HA) and Distributed Resource Scheduler Cluster (DRS).
High-availability Cluster
HA cluster means that a certain number of physical servers are combined into a cluster and virtual machines are running on them. In the event that one of the hosts fails, the virtual machines will run on the other servers in the group, on which there has been previously allocated space. As a result, downtime is equal to the booting time of the virtual machine operating system.
If you want to reduce downtime to a minimum, we recommend using VMware Fault Tolerance technology. The basic idea of this option is creating a synchronous replica of a virtual machine on another server and instantly switching to it when the main host fails.

Distributed Resource Scheduler Cluster
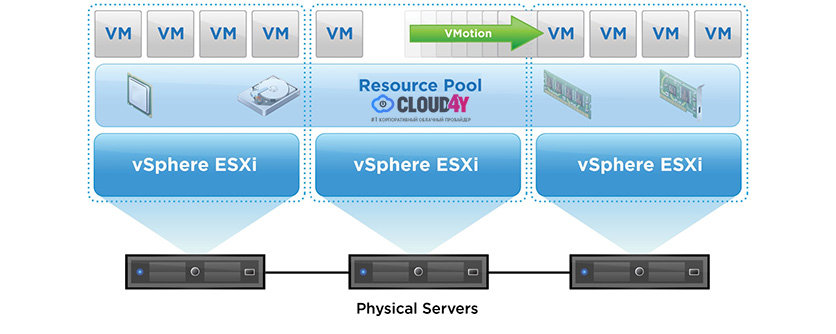
VMware DRS technology is used for load balancing in a cluster. For this purpose, the cluster resources are initially combined in a pool and then load balanced between hosts by moving virtual machines. DRS can recommend moving with the necessary confirmation from the administrator or do it automatically. This happens with the use of the vMotion live migration utility, thanks to which the migration does not require VMs to stop. Users continue working with one VM instance until the data is transferred to another host. At the last moment, the latest changes are copied from RAM, the user can observe a slight short-term decrease in system performance and after a moment is already working with the same VM, which in fact is already on another physical server.
In the case of VMware cluster, a group of two or more ESXi servers is centrally managed by VMware vCenter Server. In fact, it is possible to create virtual machines on the same host with the VMware ESXi hypervisor installed, but you will not have HA, DRS, and other features. You will simply be able to "divide" your physical server into several virtual ones, and its non-functionality will mean the downtime of all VMs.
VMware vSphere platform
To use all cluster capabilities, you need the VMware vSphere platform, which includes ESXi-host management and storage server – vCenter Server. You will also need to connect a data storage system to build a cluster. It contains partitions with virtual machine files in a special cluster file system VMFS, which are available for reading and writing to all ESXi-host of the cluster. Due to the storage in one place and the VM's independence from the physical platform, rapid movement, and recovery with HA, DRS, FT, vMotion is obtained.
Simply put, VMware vCenter Server is a set of services and a database. Each of the services deals with its own specific list of tasks and interacts with other ESXi services and/or hosts. vCenter Server is a kind of command post to which ESXi hypervisors on hosts report. They communicate with each other via VPXA host agents. You can do even more from the vCenter Server control panel than connecting directly to ESXi. If you are able to create/delete virtual machines in ESXi, with vCenter Server you can additionally create and configure a cluster and all necessary cluster options for them, some of which are described above.
VMware vCenter Server can run on a separate physical server or inside a virtual machine on the same host that it manages.
VMware IaaS
The deployment of such infrastructures requires large investments. To use all the features that increase fault tolerance and reliability of the system, you need to buy at least two servers and storage and license for the VMware VSphere platform. Installation, configuration, and administration of VMware cluster will also require special knowledge and skills, as well as time and financial investments.
The best solution, in this case, is to use cloud technologies, in particular, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS). Cloud provider provides the necessary network and server equipment located in a secure data center. IT-engineers help with any technical issues. As a result, businesses can take advantage of virtualization in a VMware cluster at an affordable cost.
Customers do not need to know the nuances of VMware vCenter Server – the provider is responsible for cluster management and physical equipment. A provider creates the required number of virtual machines with the right characteristics and operating systems, routed and isolated networks with any topology, set up flexible Firewall rules, and much more. Customers only manage their virtual data centers. This is done via a convenient self-service portal VMware vCloud Director.
The cloud will free you from purchasing at least two servers, storage, and licenses. In addition, no configuration is required. We at Cloud4Y strongly believe in the stability and performance of our services that we are willing to give our customers a legally guarantee, SLA 99.982%. This means that the maximum possible service unavailability under the agreement is no more than 15 minutes per month. In addition, Cloud4Y sets the minimum acceptable CPU and RAM system performance. The number of MIPS per vCPU is at least 2900, which guarantees the claimed CPU performance. The oversubscription of physical RAM is prohibited.
Thus, the Configured Virtual RAM that the Guest OS will view is 100% dedicated physical memory, which is available to the virtual machine at any given time. This creates conditions whereby cloud servers, in terms of performance can fully replace the physical server with the appropriate characteristics for the clients, and thanks to virtualization in the cluster, the reliability and fault tolerance can be higher than in the case of using their own hardware.
Try out the cluster-related solution in your environment. To get a free trial, contact our sales team or submit a request.




